Claude Code for Beginners: Step-by-Step AI Coding Tutorial


Python is an interpreter, which converts to byte-code when it first encounters the .py module. It is portable. And, it is a one-time job.
IN THIS PAGE
1 - What's an Interpreter?
Python interpreter converts source-code to byte-code when you first execute it is non-runnable code. The only software can process that code. During Python installation, a virtual environment will create. This environment can parse the byte code.
2 - What're the differences Between Bytecode and Machine Code?
3 - How does Python Interpreter Work?
Self-read flow chart. The smiley is byte-code. It uses other libraries and create byte-code.
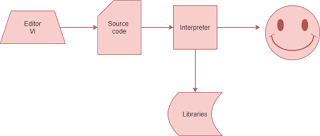 |
| Execution flow of Interpreter |
Interpreter and Libraries.
Interpreter.
The process of the interpreter is BlackBox to the programmer. The interpreter will create a .pyc module. It will then be input to PVM (Python Virtual Machine). So you don't need to interpret it when you invoke next time.
The PVM (Python Virtual Machine) is just like JVM in Java, a run-time environment, which executes Byte-code and gives you output. Here are 4 Python Oops Concepts.
Libraries.
During the Python installation, you can see a lot of other libraries do install. These libraries help the interpreter work smoothly.
A Flowchart that shows how Python interpreter uses the Libraries to create byte code.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks for your message. We will get back you.